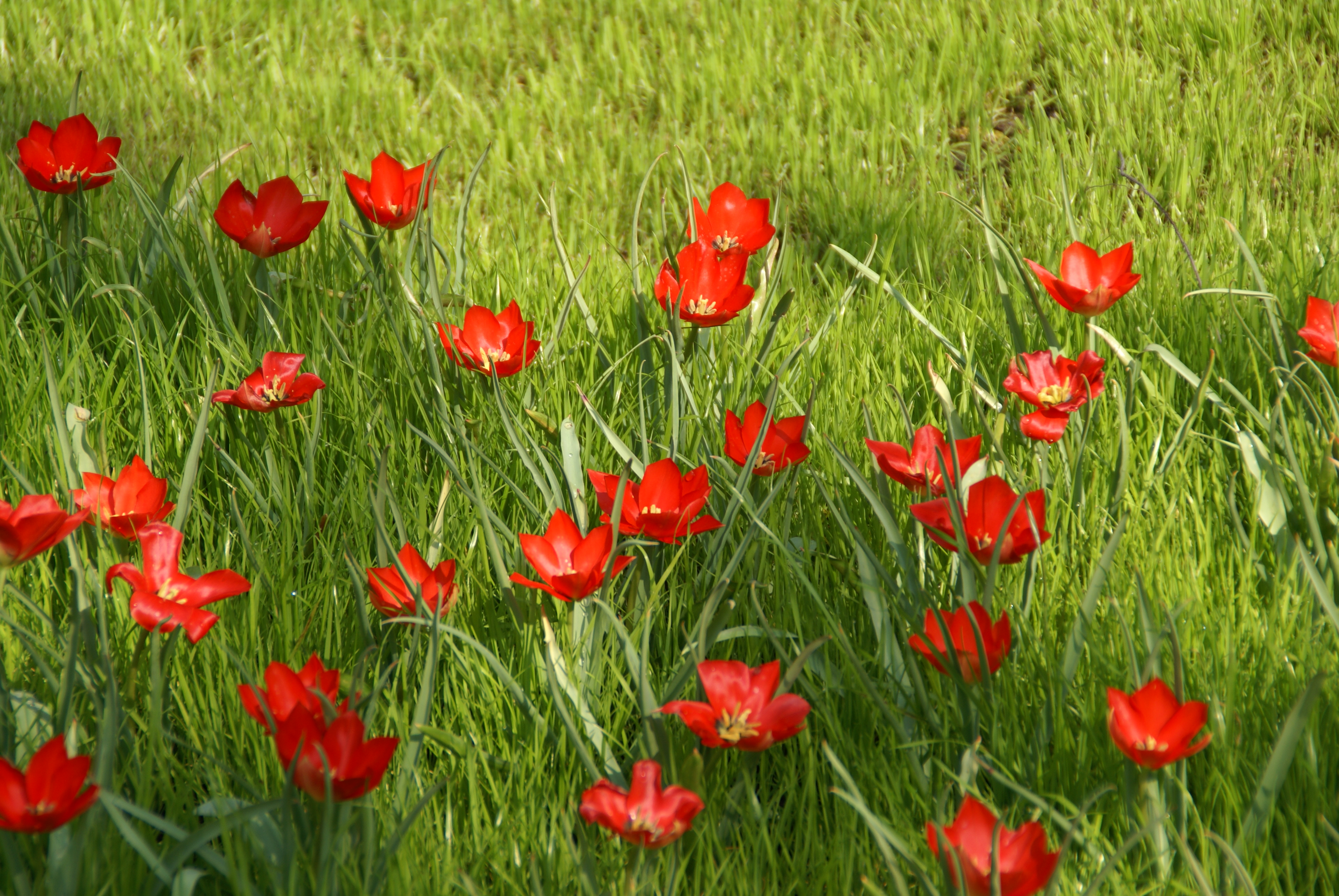
Planting flower bulbs
Planting flower bulbs
Spring flowering bulbs have to be planted in autumn because they need a cold period to flower in the spring. Preferably plant them before November 1 so they have enough time to make roots. A good root system ensures that they come through the carefree winter. It is best to plant the bulbs as soon as possible after purchase. If you have to store them for a while, make sure they are kept dry and cool (between 10 and 15 degrees Celsius).Hier zijn wat professionele tips voor planten:
Our assortment
Flower bulbs can be applied in many different ways, depending on the ultimate goal:
Our range can be divided into 2 groups:
As perennial planting:
We call this 'long-term flowering' and mean that once-planted spring bulbs remain in the ground after flowering and have the time to die off and prepare for a next growing season underground. Spring bulbs that are applied in this way thus follow the same cycle as perennials. Often, spring bulbs that are processed in this way are part of an existing perennial planting such as a permanent plant, shrub or rose border. In this situation it is essential to coordinate the colors of the flower bulbs as well as those of bulbs and permanent planting.
Bulbs that are suitable for naturalization have just a little more to offer than the bulbs that fall under the heading of 'long-term flowering'. Expansion bulbs remain in the ground after flowering and also come back every year, but as an additional benefit they expand, provided they are planted under ideal conditions (light and air). Bulbs for naturalizing can function independently, such as snowdrops and crocuses in lawns and grass verges, but they can also be part of an existing plant, for example in planters with ground cover plants under trees and shrubs.
How to plant? Many spring flowering bulbs will want to grow in full or partial sunshine. Flower bulbs grow almost in any environment, provided it has good drainage. Flower bulbs rot when they are in the water for a long time, so avoid environments that flood a lot, such as the foot of hills or under the drainage.
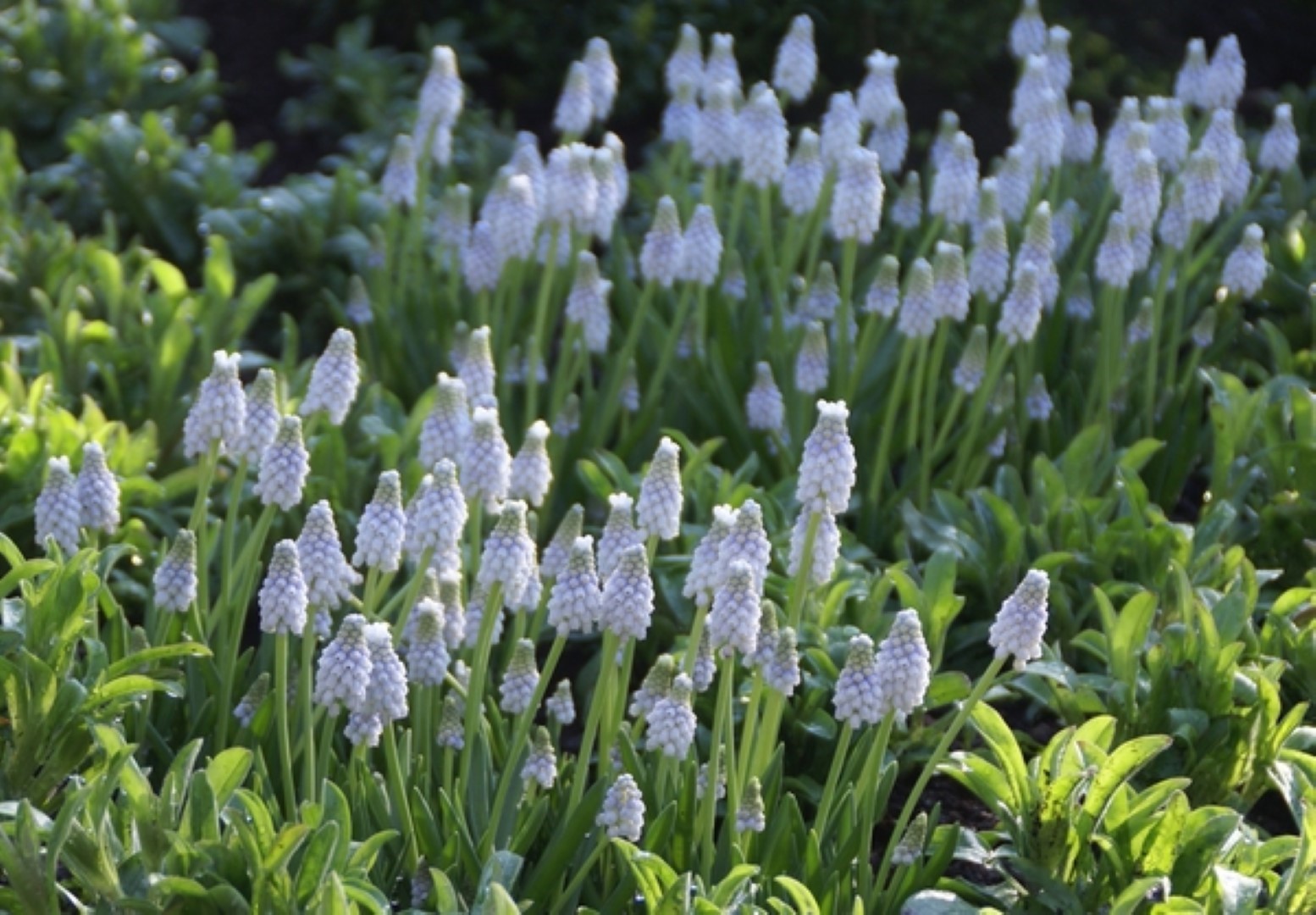

Choose a planting spot
Dig a hole for bed planting or individual holes for individual planting of bulbs or smaller clusters. To see how deep you have to plant, consider the width of the bulb. The rule is: the planting depth is equal to 2 x the width of the flower bulb. (example: a 2cm wide bulb gets a layer of 4cm high above it)
Open the ground a bit and remove weeds and small stones. Push the bulbs gently into the ground with the pointy side up. Put large bulbs, 7 to 20 cm apart and small bulbs 3 to 7 cm. Actually, nothing can go wrong because even upside down bulbs are still above the ground. Cover the bulbs with soil and water when the soil is not wet yet.
Tips for naturalizing
Many of our special flower bulbs are suitable for naturalization.
Every bulbous or tuberous plant needs - in order to be able to develop optimally - its own location, where the plants can grow undisturbed and then be able to withdraw in peace, without the leaf becoming so indispensable for the plant during die away It is furthermore important that during the period that the leafs has withdrawn, the underground parts are going through a rest period. For example, crocuses are planted in large numbers in lawns in advance so that they feel at home and can also maintain themselves, partly due to the fact that the soil is rather dry during the rest of the tubers. The condition is that the leaf can fully extend and the grass that is not mowed in the spring, after the bulbs have shown their floral splendor. For many, it is rather difficult not to use the mower or scissors to put an end to the rather messy impression that a non-mowed lawn offers.
After the flowering the leaf development increases strongly and seed is also formed which should be given ample opportunity to ripen. The seeds that fall between the plants will find a good breeding ground there to germinate, resulting in an increase in the number and in the long run considerably more flowers.
Exceptions
Not all bulbous and tuberous plants, which after being planted once and left to their fate, have the ability to annually exuberant bloom and also to multiply again. Through extensive research in recent years we have come to the conclusion that many flower bulbs are suitable for long-term flowering when planted in a light and sunny environment. Of course these are the famous Allium, Anemone, Chionodoxa, Corydalis, Cyclamen, Fritillaria, Crocus, Narcissus, Muscari, Scilla, Triteleia etc ..
Plant position
For the growth of flower bulbs, a number of specific places suitable for this purpose are eligible. Apart from the fact that they have to cover a sufficiently large surface, they also have to be overseen from different fields of view. Grass fields are very suitable. In addition, wide edges along shoreline groups are also eligible. A woody part of the garden can be significantly enlivened with the application of a massive planting of the species that naturally belong there
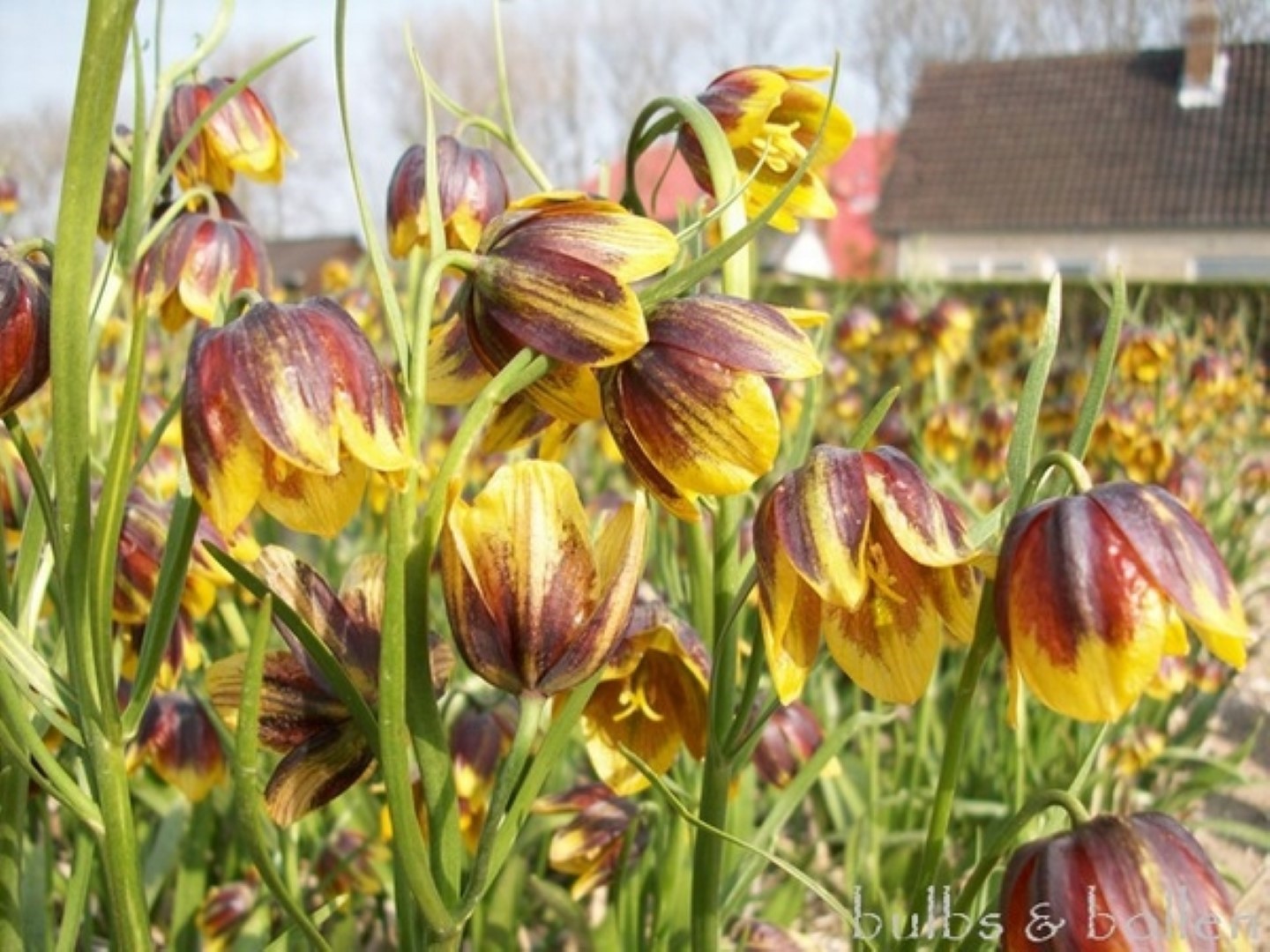

The soil
Before starting to plant, it must be checked if the soil is suitable for the development of flower bulbs. Water management, humus content and acidity (pH) is also important. If the drainage does not function properly, this must be remedied. The humus content is increased by the application of organic fertilizers and / or compost. This is also excellent for the heavier loam and clay soils. The pH, which must be around 6-6.5, can be increased by applying lime. It is reduced by adding peat.
Fertilization
A tailor-made fertilization prevents plants from becoming ill and becoming susceptible to diseases and pests, resulting in less use of pesticides. Proper fertilization also ensures a good soil structure.
There is a choice of various fertilizers
• Compost and animal manure. These are organic fertilizers. They are, as described earlier, also good soil improvers.
• Natural fertilizers that are given as an addition to organic manure.
• Fertilizer.
The type of fertilization to be chosen depends on the type of planting and the time when it can be fertilized. Plants and bulbs that propagate on their own are in their natural location. Nature is in balance here. The type of soil, structure, water management and planting fit together perfectly here. It is not customary to fertilize in a balance situation.
It may be apparent from a number of phenomena (often visible in the leaf of plants) that there is a shortage of a particular nutrient. Then the use of additional fertilizers is a recommendation. These fertilizers must be organic and therefore fit better in the natural environment in which the plants are located.
Additional fertilizers supplement specific shortages in plant fertilizers from organic fertilizers, such as phosphorus fertilizer (phosphorus) and vinassekali (kali: waste product from the food industry). Finally, there are fertilizers with lime, such as maërl (coral algae lime), which regulate the acidity of the soil.
If this application is carried out once a year, it is important for the flower bulbs that this fertilization takes place immediately after flowering.
Mow
The bulbs that are planted in grass can only be mowed once the above-ground parts of the bulb have died out completely. The rule for mowing is that it can be started on average 6 to 8 weeks after the flowering period.